Hoarseness is a common symptom characterized by changes in voice quality, such as breathiness, raspiness, or strain. Understanding how our voice works and the various conditions that can lead to hoarseness is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment. Let’s explore the implications of hoarseness, from its underlying causes to available treatments.
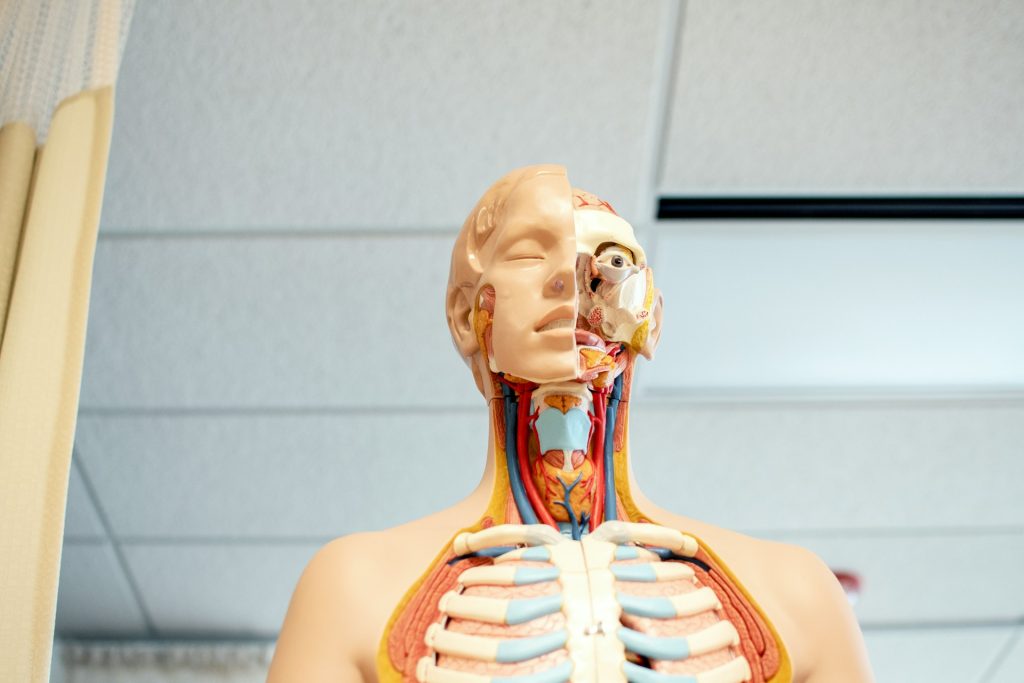
How Does Our Voice Work?
The production of sound in our voice begins with the vibration of the vocal folds, located in the larynx or voice box. These folds, composed of muscle tissue, come together when we speak, allowing air from the lungs to pass through and create vibrations. The resulting sound waves resonate through the throat, nose, and mouth, producing the unique qualities of our voice. Factors such as vocal fold tension and the shape of resonating cavities contribute to variations in pitch, volume, and tone.
When Should I See My Doctor?
Persistent hoarseness lasting more than three weeks warrants a visit to the doctor, especially if it occurs without a preceding cold or flu. Additional symptoms such as coughing up blood, difficulty swallowing, or pain while speaking may indicate underlying issues requiring medical attention. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.

How Will My Doctor Diagnose the Cause?
Your doctor will assess your medical history and conduct a physical examination to determine the cause of hoarseness. In some cases, referral to an otolaryngologist may be necessary for further evaluation using techniques like endoscopy to visualize the vocal folds. Specialized tests may also be recommended to assess vocal irregularities and airflow, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Common Causes and Treatments
Hoarseness can stem from various conditions, each requiring tailored treatment approaches:
Laryngitis: Often caused by viral infections or allergies, laryngitis results in temporary swelling of the vocal folds. Treatment may include rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications for symptom relief.
Misuse or overuse of the voice: Excessive strain on the vocal folds from activities like yelling or prolonged speaking can lead to hoarseness. Rest, hydration, and voice therapy are often recommended to alleviate symptoms.
Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD): Stomach acid refluxing into the throat can irritate the vocal folds, causing hoarseness. Lifestyle modifications and medications to reduce acid reflux are typical treatments.
Vocal nodules, polyps, and cysts: Benign growths on the vocal folds can result from vocal abuse or injury. Voice rest, therapy, or surgical removal may be necessary, depending on the severity.
Vocal fold hemorrhage: Rupture of blood vessels on the vocal folds requires immediate rest and medical evaluation to prevent further damage.
Vocal fold paralysis: Dysfunction of vocal fold movement due to neurological conditions or injury may necessitate voice therapy or surgical intervention.
Neurological diseases: Disorders affecting the brain’s control of throat muscles can cause hoarseness, often requiring specialized treatment approaches.
Other causes: Thyroid issues, laryngeal cancer, or recurrent respiratory papillomatosis may also manifest as hoarseness, necessitating comprehensive evaluation and management.
Ongoing Research Efforts
Researchers are actively investigating novel approaches to understanding and treating hoarseness. Projects aimed at promoting voice hygiene, exploring genetic factors, and developing targeted interventions offer promising avenues for future advancements in hoarseness management.

Hoarseness is a multifaceted symptom with diverse underlying causes and treatment modalities. By recognizing the signs, seeking timely medical evaluation, and exploring effective interventions, individuals experiencing hoarseness can regain vocal health and quality of life. Working closely with healthcare providers and staying informed about ongoing research initiatives are crucial steps in addressing hoarseness and promoting optimal vocal well-being.